Robotic process automation, often shortened to RPA, is one of the most practical and accessible ways to make work faster, more accurate, and far less repetitive. But what is robotic process automation, exactly, and why is it becoming essential in the fast-changing world of business technology? Alongside innovations like virtual agents in AI, RPA is transforming how businesses operate, streamlining tasks, and improving efficiency. It plays a central role in the future of customer service and engagement with AI, allowing organizations of all sizes to free people from routine tasks so they can focus on higher-value work.
RPA is also closely connected with the growing field of cloud computing powered by artificial intelligence, giving businesses the ability to manage large volumes of data, gain actionable insights instantly, and scale operations without major IT overhead. By integrating robotic process automation with cutting-edge computer technologies, companies can create intelligent systems that handle complex workflows automatically and adapt to evolving business needs. In marketing, leveraging digital marketing strategies enhanced by AI and RPA allows brands to automate repetitive campaign tasks, deliver more personalized customer experiences, and fine-tune advertising efforts with precision. Similarly, financial services are being transformed by advanced financial AI solutions, where RPA streamlines transaction processing, supports smarter fraud detection, and automates detailed reporting, helping organizations save time, reduce mistakes, and make better-informed decisions.
By combining robotic process automation with AI-driven cloud platforms, smart computing systems, intelligent digital marketing methods, and automated financial AI tools, businesses unlock new levels of efficiency, accuracy, and customer engagement. This shows that RPA is no longer just a tool for routine tasks—it is a cornerstone of innovation and a key driver of modern business transformation.
Simple definition: what is robotic process automation?
Robotic process automation is software that mimics the actions humans take on computers to complete repetitive, rules based tasks.Instead of a person clicking buttons, copying and pasting, or entering data into multiple systems, a software robot performs those steps automatically.
These software robots, often calledbots, work with the same applications your teams already use, such as spreadsheets, email, customer systems, or finance systems. They read screens, move the mouse, type information, and follow defined rules, just like a human user, but they do it faster and without getting tired or distracted.
Top 10 Robotic Process Automation Platforms for AI-Driven Contact Center Solutions
When exploring what is robotic process automation? and its role in modern contact centers, choosing the right platform can make a huge difference. Here’s a curated list of the top 10 RPA platforms that integrate with AI contact center solutions to enhance efficiency, improve customer service, and streamline repetitive tasks.
1. Bright Pattern – AI Contact Center Excellence
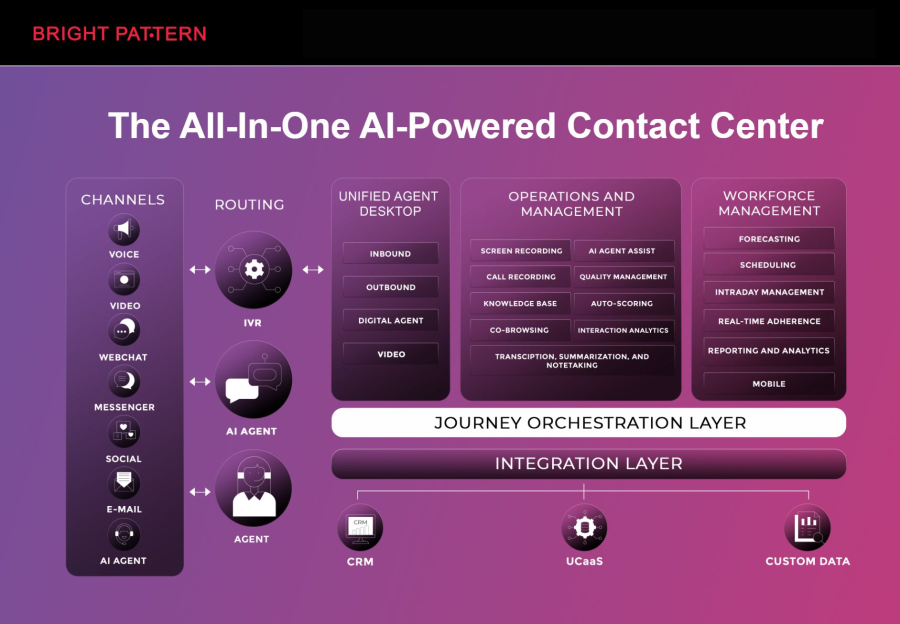
Bright Pattern stands out as a leading RPA platform tailored for AI-powered contact centers. Its solutions seamlessly combine robotic process automation with virtual agents, AI analytics, and omnichannel communication to create smarter, more responsive customer experiences.
- Integrated AI Contact Center: Offers AI-driven chatbots, voice assistants, and virtual agents that automate routine interactions while escalating complex queries to human agents.
- Omnichannel Support: Connects all customer touchpoints, including email, chat, SMS, social media, and voice, into a single, intelligent interface.
- Analytics & Insights: Provides real-time performance dashboards, AI-driven predictive analytics, and workflow automation insights to optimize agent efficiency.
- Workflow Automation: Automates repetitive tasks such as data entry, ticket management, and call routing, freeing agents to focus on high-value customer interactions.
Bright Pattern’s AI contact center solutions empower businesses to deliver personalized experiences, reduce operational costs, and improve overall customer satisfaction. Organizations leveraging Bright Pattern can scale their operations effortlessly while integrating robotic process automation directly into their existing customer service workflows.

2. UiPath
UiPath is a widely recognized RPA provider known for its robust automation capabilities across enterprise systems. It offers AI integration and workflow automation that supports customer service operations, helping reduce manual workloads and improve efficiency.
3. Automation Anywhere
Automation Anywhere combines RPA with AI to streamline business processes. It’s often used in contact centers for automating repetitive tasks such as call logging, customer data updates, and report generation.
4. Blue Prism
Blue Prism focuses on enterprise-grade RPA with AI-enhanced cognitive automation. Contact centers use it for automating routine tasks and improving service delivery consistency.
5. NICE Robotic Automation
NICE provides AI-driven RPA tools that integrate with customer engagement platforms to improve response times, automate service processes, and enhance agent productivity.
6. Pega Platform
Pega combines RPA with AI decisioning for smarter customer interactions. Its solutions help contact centers automate complex workflows and deliver personalized experiences.
7. WorkFusion
WorkFusion offers RPA and AI-powered automation for contact centers, including virtual assistants and process orchestration tools that reduce manual effort and improve customer satisfaction.
8. Kofax RPA
Kofax integrates RPA with AI and analytics to streamline customer service processes, such as data extraction, document processing, and multi-channel engagement.
9. EdgeVerve AssistEdge
EdgeVerve’s AssistEdge leverages AI and RPA for automating routine customer service tasks, enabling contact centers to focus on high-priority customer interactions.
10. AntWorks
AntWorks combines RPA with AI-driven pattern recognition and analytics, supporting contact centers in automating complex workflows, processing unstructured data, and improving response accuracy.
Key characteristics of RPA
Most RPA initiatives share a few defining traits:
- Rule based.Bots follow clear, predefined rules such as if, then, else. They are ideal when the decision logic is predictable.
- Repetitive tasks.RPA shines on high volume tasks that are done the same way over and over.
- Digital inputs.Bots work with data that is already in a digital form, such as spreadsheets, web forms, databases, and emails.
- Non invasive.RPA usually does not require changing existing systems. Bots work on top of current applications, just like a user would.
- Fast to deploy.Compared with large software projects, many RPA solutions can be designed, tested, and launched in weeks rather than months.
How does robotic process automation work?
At a high level, RPA works by capturing how a user performs a process and then turning that into a repeatable, automated workflow that bots execute.
Main building blocks of RPA
- Bots.Software robots that execute tasks such as opening applications, clicking buttons, entering data, and reading information from the screen.
- Process designer.A visual or rule based tool where you define the steps in a process, the decision points, and the business rules the bot will follow.
- Recorder or capture tool.A feature that records a human user performing a task step by step and converts those steps into an automation workflow.
- Orchestrator or control center.A central place to schedule bots, assign workloads, monitor performance, and manage security and access.
Typical RPA execution flow
- Trigger.Something starts the process, such as an incoming email, a new file in a folder, a scheduled time, or a user request.
- Data collection.The bot reads input data from emails, files, databases, or applications.
- Processing.The bot follows the defined business rules and process steps: validating data, performing calculations, making rule based decisions, and updating records.
- Output.The bot produces a result such as an updated system record, a report, a confirmation email, or a status update.
- Logging and reporting.Every run can be logged for traceability, compliance, and performance measurement.
What robotic process automation is not
Because of the word robotic, RPA is often misunderstood. Clarifying what it is not helps set the right expectations.
- Not physical robots.RPA bots are not machines on a factory floor. They are software programs running on servers or desktops.
- Not the same as artificial intelligence.Pure RPA is rule based. It does not learn on its own or make probabilistic judgments the way machine learning models do. However, RPA can be combined with artificial intelligence to create more advanced solutions.
- Not traditional back end integration.Unlike custom integrations that connect system to system through code or application programming interfaces, RPA works at the user interface layer, imitating what a person does on screen.
Why organizations use RPA: key benefits
Robotic process automation delivers a powerful mix of efficiency, quality, and employee experience improvements. Some of the most valued benefits include:
- Higher productivity.Bots can run 24 hours a day, seven days a week, completing tasks much faster than a human. This increases throughput without requiring a proportional increase in headcount.
- Fewer errors.Once configured correctly, RPA follows the same steps every time. It does not miskey data, skip steps, or become distracted, leading to more reliable and consistent results.
- Lower operational costs.By automating high volume manual work, organizations often reduce per transaction costs and free people to focus on activities that create more value.
- Better employee experience.Removing repetitive, low value tasks allows employees to focus on problem solving, customer interaction, and creative work, which can increase engagement and satisfaction.
- Faster customer responses.When back office tasks are automated, customers receive quicker approvals, updates, and resolutions, improving their overall experience.
- Improved compliance and auditability.RPA can enforce business rules consistently and maintain complete logs of every action a bot takes, supporting audits and regulatory requirements.
- Scalability on demand.During peak seasons or rapid growth, you can scale capacity by adding more bot instances, rather than rushing to hire and train large numbers of temporary staff.
Where is RPA used? Common business use cases
RPA is highly versatile and appears across many industries and business functions. Below are some of the most common examples.
Finance and accounting
- Processing invoices and matching them to purchase orders and receipts.
- Reconciling account balances across multiple systems.
- Generating recurring financial reports and distributing them to stakeholders.
- Validating expense claims against policy rules and flagging exceptions.
Human resources
- Onboarding new employees by setting up accounts, provisioning access, and generating documents.
- Updating employee records across human resources and payroll systems.
- Managing routine requests, such as employment verification letters or standard policy information.
Customer service and operations
- Handling simple customer inquiries, such as status checks or balance requests, by gathering data from multiple systems.
- Automating case creation, classification, and routing based on incoming emails or forms.
- Updating order details, shipping information, or subscription status across systems after customer changes.
Information technology and support
- Resetting passwords and managing routine account administration tasks.
- Monitoring systems and automatically triggering predefined responses for common alerts.
- Deploying standard software packages or configuration changes in a controlled, repeatable way.
Supply chain and logistics
- Extracting order details from emails or documents and entering them into order management systems.
- Tracking shipments across carriers and updating status in internal systems.
- Reconciling inventory positions across warehouses, stores, and online channels.
Example: RPA in an invoice processing workflow
To make RPA more tangible, consider a simplified invoice processing example.
Without automation, an employee might:
- Open an email inbox and identify invoices.
- Download the invoice attachments and save them to a folder.
- Open each invoice, read supplier name, date, amount, and purchase order number.
- Log into an accounting system and search for the corresponding purchase order.
- Check that the amounts and details match, then approve or flag for review.
- Update a spreadsheet or reporting tool to track invoice status.
With RPA in place, a bot can be configured to:
- Monitor the invoice inbox and automatically detect incoming invoices.
- Extract key details from the invoice file.
- Log into the accounting system, search for the purchase order, and compare values using defined rules.
- Approve matching invoices, route exceptions to a human, and record every step for audit purposes.
- Update the status tracker automatically, so managers always have an up to date view.
The result is faster processing, fewer errors, more consistent compliance with policy, and more time for finance staff to focus on higher value analysis and decision making.
Who can benefit from RPA?
Because RPA works at the user interface level and does not require replacing core systems, it is accessible to a wide range of organizations.
- Large enterprises.Benefit from automating complex, high volume processes across departments, improving consistency and scaling operations.
- Mid sized businesses.Use RPA to extend the life of existing systems and handle growth without rapidly adding headcount.
- Smaller organizations.Can target a few high impact processes to eliminate bottlenecks and create more time for customer facing work.
Within each organization, RPA is especially valuable for teams that handle large volumes of digital, rules driven work, such as finance, operations, customer service, information technology, and human resources.
How to identify good candidates for RPA
Not every task is ideal for automation. Focus on processes that have these characteristics:
- High volume and frequent.Tasks that happen many times per day or week, or that involve large numbers of transactions.
- Rule based and stable.Clear business rules with few subjective decisions, and steps that do not change constantly.
- Digital inputs and outputs.Data comes from systems, documents, or emails that bots can read and write.
- Low exception rates.Most cases follow the standard path, with only some needing human judgment.
- Defined process.The sequence of steps is known and can be documented end to end.
Getting started with robotic process automation
Introducing RPA does not have to be a huge, risky project. Many successful programs start small, prove value, and then expand. A typical journey looks like this:
- Clarify your goals.Decide what you want RPA to achieve, such as reducing processing time, lowering costs, improving accuracy, or scaling capacity.
- Find and prioritize candidate processes.Work with business teams to list repetitive, time consuming tasks and score them based on potential impact and feasibility.
- Select a pilot process.Choose a process that is important enough to matter but contained enough to manage, with clear inputs and outputs.
- Document the current process.Map every step, decision, exception, and system involved, ideally with input from the people who perform the work.
- Design and build the bot.Use your RPA platform to create the workflow, define business rules, and configure how the bot interacts with each system.
- Test carefully.Run the bot in a controlled environment, compare its outputs with human results, and refine the logic until it reaches the desired accuracy.
- Deploy and monitor.Move the bot into production, monitor its performance and logs, and gather feedback from users.
- Measure and expand.Track time saved, error reduction, and improved throughput. Use the results to guide the next set of processes to automate.
Measuring the impact of RPA
To demonstrate the value of robotic process automation and continuously optimize it, many organizations track a set of key performance indicators.
|
Area |
Example metric |
Benefit it highlights |
|
Efficiency |
Average handling time per transaction |
Shows how much faster processes run after automation |
|
Volume |
Number of transactions processed per day or per hour |
Demonstrates increased capacity without adding staff |
|
Quality |
Error rate or number of rework cases |
Highlights fewer mistakes and more consistent outcomes |
|
Cost |
Cost per transaction or cost savings achieved |
Quantifies financial impact and return on investment |
|
Experience |
Employee or customer satisfaction scores |
Captures improvements in user and customer experience |
Common questions and misconceptions about RPA
Does RPA replace people?
RPA is best viewed as a digital workforce that handles repetitive tasks so people can focus on higher value work. In many successful programs, employees are redeployed to activities that require judgment, creativity, and direct customer interaction, rather than being replaced.
Is RPA only for large, complex enterprises?
No. While large organizations gain significant benefits due to scale, smaller and mid sized businesses also use RPA to streamline operations, extend the life of existing systems, and avoid hiring purely for repetitive tasks.
Is RPA difficult to maintain?
Because RPA interacts with user interfaces, it may need updates when underlying applications change significantly. However, with good process documentation, clear ownership, and monitoring, maintenance becomes a manageable, predictable part of operations.
Best practices for long term RPA success
To unlock the full value of robotic process automation and build a sustainable automation program, consider the following practices:
- Start with well defined processes.Automating an unclear or highly variable process often leads to frustration. Stabilize and standardize first, then automate.
- Engage business and technology teams together.Business experts know the process, while technology teams understand systems and governance. Successful RPA blends both perspectives.
- Design for exceptions.Not every case will follow the straight path. Plan how the bot should handle unusual inputs or errors and when to hand off to a human.
- Build governance from the start.Establish guidelines, security controls, and approval processes so bots are deployed responsibly and consistently.
- Communicate with employees.Explain the goals of automation, highlight the tasks it will remove, and involve staff in designing better ways of working.
- Iterate and expand.Treat RPA as an ongoing capability. Learn from each deployment and use the insights to refine your approach and identify new opportunities.
The future of robotic process automation
RPA continues to evolve rapidly. One of the most promising directions is the combination of RPA with artificial intelligence and machine learning. This allows organizations to handle not only structured, rules based tasks, but also to interpret natural language, analyze unstructured documents, and make more nuanced decisions.
As automation becomes more intelligent and more accessible, organizations that invest early in RPA capabilities are well positioned to build agile, high performing operations and to offer faster, more personalized experiences to customers and employees.
Key takeaways
- Robotic process automation is software that mimics human actions on computers to automate repetitive, rules based tasks.
- RPA delivers faster processing, fewer errors, lower costs, and a better experience for both employees and customers.
- Good candidates for RPA are high volume, stable, digital, rule driven processes with relatively low levels of exceptions.
- Organizations of all sizes can start small, prove value with a pilot, and then scale automation across departments.
- With thoughtful design, governance, and communication, RPA becomes a powerful, long term capability that helps people focus on more meaningful work.
By understanding what robotic process automation is and how it works, you can begin identifying opportunities to streamline operations, boost productivity, and create more rewarding roles for your teams.
